
14 Sep HbA1c Guidelines for Diabetes Control
What is HbA1c?
HbA1c serves as an indicator of diabetes control. It refers to your blood glucose control over the last 3 months and is an ideal way to indicate the risk of complications. Ideally, HbA1c range falls <7%. But, for people without diabetes, normal range is between 4-5.6% and HbA1c levels between 5.6-6.5% indicate good control of blood glucose. HbA1c levels of ≥7% indicate a high risk in diabetes complications.
Keeping your HbA1c <7% can greatly reduce your risk of developing diabetes complications
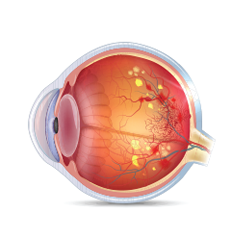 |
Retinopathy (Eye Disease) It is caused by small vessel damage to the back layer of the eye, the retina, leading to progressive loss of vision and even blindness. |
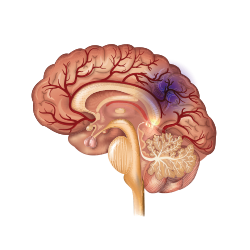 |
Alzheimer’s Disease It is a progressive and fatal brain disorder that gradually destroys a person’s memory and ability to learn, make judgements, communicate and carry out daily activities. Statistic: In America, 29% of patients with Alzheimer’s disease are diabetic. |
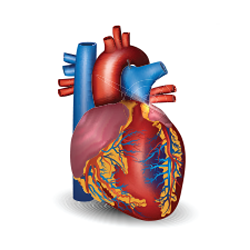 |
Cardiovascular Disease It is caused by the narrowing of arteries due to high blood glucose that lead to decreased blood flow to heart muscle (causing a heart attack), or to brain (leading to stroke), or to extremities (leading to pain and decreased healing of wound). |
 |
Neuropathy (Nerve Disease) It is caused by nerve damage due to high sugar in blood and decreased blood flow to nerves from damaged small blood vessels. This can lead to sensory loss, damage to limbs, and importance in diabetic men. |
 |
Nephropathy (Kidney Disease) It is caused by damage to small blood vessels in kidneys and eventually leads to kidney failure. Statistic: In Malaysia, nearly 60% of all new patients accepted for renal dialysis are diabetics. |




No Comments